Welcome to the great outdoors! If you’re planning on exploring the desert, it’s crucial to understand the environment and know what kind of food sources are available. The desert may seem like a harsh and barren landscape, but it’s actually home to an array of delicious and nutritious foods that many people may not be aware of.
In this article, we’ll be exploring the diverse range of foods that grow in the desert, from prickly cactus pads to protein-packed beans. So, if you’re ready to learn about the hidden gems of the desert and discover new ways to survive and thrive in the great outdoors, read on!
Here is a list of what foods grow in the desert.
1. Mesquite
Mesquite is a common tree found in the deserts of North America and has been used as a food source by indigenous people for thousands of years. The tree’s bean pods, also known as mesquite pods or mesquite beans, are edible and have a sweet, nutty flavor that is similar to molasses or caramel.
Mesquite beans are high in protein, fiber, and essential nutrients, making them a valuable food source for survivalists and outdoor enthusiasts. The beans can be ground into flour and used to make bread, cakes, and other baked goods. The flour can also be added to smoothies or used as a thickener for soups and stews.
To harvest mesquite beans, wait until the pods are fully ripe and dry. The pods will be brown, and the beans inside will rattle when shaken. The pods can be harvested by hand or collected from the ground. After harvesting, the pods should be roasted to remove any bitterness and to enhance the beans’ flavor.
To roast mesquite pods, place them in a single layer on a baking sheet and bake in the oven at 350°F for 10-15 minutes, or until they are lightly browned and fragrant. After roasting, remove the pods from the oven and let them cool. Once cooled, the pods can be cracked open, and the beans inside can be removed.
In addition to their culinary uses, mesquite trees are also valuable for their wood, which can be used for smoking meats and other foods. Mesquite wood gives off a strong, smoky flavor that is perfect for barbecuing and grilling.
2. Agave
Agave plants are a common sight in many desert regions, known for their spiky leaves and tall flower stalks. However, what many outdoor enthusiasts may not know is that agave plants are also a source of food and drink.
Agave plants are used to make a variety of products, including agave nectar, tequila, and mezcal. Agave nectar is a popular sweetener used in many recipes, including baked goods and drinks. Tequila and mezcal, on the other hand, are alcoholic beverages made from the distilled sap of agave plants.
To harvest agave plants for food and drink, the leaves are typically removed, leaving only the core, or “piña,” which contains the sweet sap. The piña is then roasted, mashed, and fermented to produce tequila or mezcal. Alternatively, the sap can be extracted from the piña and used to make agave nectar.
Aside from their culinary uses, agave plants also have medicinal properties. The sap has been used by indigenous communities for centuries to treat a variety of ailments, including wounds, fever, and digestive issues.
In addition to their practical uses, agave plants are also important ecologically. They are often used to help prevent soil erosion, as their deep root systems can help stabilize the soil in desert environments. They also provide a habitat for a variety of wildlife, including birds and insects.
Despite their many benefits, it’s important to note that agave plants can take several years to mature and may be vulnerable to overharvesting. As such, it’s important to use agave products responsibly and support sustainable harvesting practices.
3. Jojoba
Jojoba is a shrub that is native to the deserts of the southwestern United States and Mexico. The plant produces a nut that contains an oil that has many benefits for both survivalists and outdoor enthusiasts.
Jojoba oil is a versatile oil that can be used for many different purposes. It is a natural moisturizer that can be used to hydrate and nourish skin and hair. It is also an effective treatment for dry and chapped lips, making it a must-have item for any outdoor adventure.
In addition to its skincare benefits, jojoba oil can also be used as a natural insect repellent. The oil contains a compound called myristic acid, which is known to repel mosquitoes, ticks, and other insects. To use jojoba oil as an insect repellent, simply apply a small amount of the oil to your skin or clothing before heading outdoors.
Jojoba oil is also a valuable ingredient in many cosmetic and skincare products, including soaps, lotions, and shampoos. Its natural moisturizing properties make it an excellent ingredient for dry and sensitive skin.
Aside from its oil, the jojoba plant also produces a nutritious seed that is edible and can be roasted and eaten as a snack. The seeds are high in protein, minerals, and vitamins, making them a valuable food source for survivalists and outdoor enthusiasts.
To harvest jojoba seeds, wait until the pods are fully ripe and dry. The pods will be brown, and the seeds inside will be hard and dark. The pods can be harvested by hand or collected from the ground. After harvesting, the seeds can be roasted and eaten as a snack, or ground into a flour and used as a gluten-free alternative to wheat flour.
4. Desert Date
Desert Date, also known as Balanites Aegyptiaca, is a small tree that grows in the deserts of Africa and the Middle East. The tree produces a fruit that has been used for centuries for its medicinal and nutritional properties.
The fruit of the Desert Date tree is oval-shaped, and when ripe, turns from green to yellow-orange. It has a tough outer skin, but inside, there is a soft, fleshy pulp that surrounds a hard, woody seed. The fruit is edible and has a sweet, somewhat sour taste.
Desert Date fruit is rich in nutrients, including vitamins A, C, and E, as well as potassium, magnesium, and calcium. The fruit also contains high levels of antioxidants, which can help to protect the body against free radicals and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
In addition to its nutritional properties, Desert Date fruit has also been used for its medicinal benefits. The fruit is believed to have antimicrobial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties, which make it effective in treating a range of conditions. In traditional medicine, Desert Date fruit has been used to treat skin disorders, respiratory infections, and digestive issues.
Aside from its fruit, the Desert Date tree also provides other valuable resources for survivalists and outdoor enthusiasts. The tree’s leaves and bark can be used to make a natural soap, while the seeds can be ground into a flour and used to make a nutritious bread.
To harvest Desert Date fruit, wait until the fruit is ripe and falls off the tree. The fruit can then be collected and eaten raw or cooked. To cook the fruit, simply cut it in half and remove the hard seed, then boil or bake the remaining flesh until it is soft and tender.
5. Chia
Chia is a type of plant that is native to Mexico and Guatemala. It is known for its tiny, black seeds that have been used for centuries as a source of nutrition and energy.
Chia seeds are rich in nutrients, including fiber, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids. They also contain minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and zinc. These nutrients make chia seeds a valuable food source for outdoor enthusiasts, as they can help to maintain energy levels and provide sustained nourishment.
In addition to their nutritional properties, chia seeds also have other benefits for outdoor enthusiasts. The seeds can be added to water to create a gel-like substance that can help to keep the body hydrated during physical activity. This is because the seeds are able to absorb large amounts of water, which helps to slow down the body’s absorption of carbohydrates and maintains a steady release of energy.
Chia seeds can also be used to make a nutritious and delicious snack for outdoor activities. Simply mix the seeds with water or other liquids to create a chia pudding or add them to trail mix for a quick and easy snack on the go.
Aside from their use as a food source, chia plants also have medicinal properties. The seeds have been used to treat a range of ailments, including digestive issues, skin problems, and inflammation.
To grow chia plants, they require well-drained soil and plenty of sunlight. The plants can be grown in pots or directly in the ground. Once the plants have matured, the seeds can be harvested by cutting the seed heads and allowing them to dry.
6. Prickly Pear Cactus
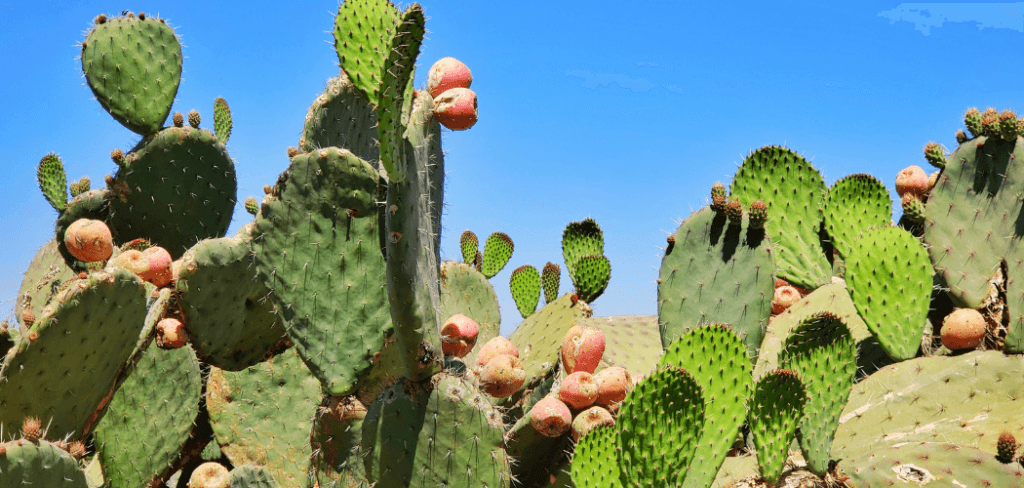
Prickly pear cactus, also known as Opuntia, is a common sight in many desert regions around the world. While it may look intimidating with its spiky exterior, this cactus actually produces a fruit that is not only edible but also packed with health benefits.
The fruit of the prickly pear cactus is known as the tunas, and they come in a variety of colors ranging from green to red to purple. They are rich in vitamin C, magnesium, and potassium, making them a great source of hydration and nourishment for outdoor enthusiasts.
To harvest the fruit, it’s important to wear gloves and use tongs to avoid getting pricked by the cactus spines. Once harvested, the tunas can be peeled and eaten raw, or cooked and used in a variety of recipes. They have a sweet, slightly tart taste and can be used to make jams, jellies, and even cocktails.
Aside from the tunas, other parts of the prickly pear cactus are also edible. The pads, or nopales, can be sliced and cooked to make a nutritious and delicious side dish. They are high in fiber, vitamin C, and calcium, making them a valuable addition to any outdoor enthusiast’s diet.
In addition to their nutritional properties, prickly pear cactus also has medicinal uses. The sap from the cactus can be used to treat minor cuts and burns, while the pads can be used to soothe sunburned skin.
Prickly pear cactus is also a hardy plant that requires minimal water and can survive in extreme temperatures. This makes it an ideal plant for desert environments, and it’s even been used in some areas for erosion control.
7. Tepary Beans
Tepary beans, also known as Phaseolus acutifolius, are a type of bean that have been cultivated in the deserts of the southwestern United States and Mexico for thousands of years. These beans are incredibly resilient, able to thrive in arid and hot environments where other crops may struggle to survive.
Tepary beans are an excellent source of protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates, making them a nutritious addition to any outdoor enthusiast’s diet. They come in a variety of colors and sizes, from small and white to large and black, and can be used in a variety of recipes.
To prepare tepary beans, it’s important to soak them overnight to reduce their cooking time and improve their texture. They can then be cooked like any other type of bean, and used in soups, stews, salads, and even baked goods.
Aside from their nutritional value, tepary beans also have cultural significance for many indigenous communities in the southwestern United States and Mexico. They have been an important part of these communities’ diets and are often used in traditional ceremonies and rituals.
In addition to their culinary and cultural uses, tepary beans also have ecological benefits. They are a nitrogen-fixing crop, meaning they can help improve soil quality and reduce the need for fertilizers. They also require less water than other types of beans, making them a more sustainable crop for desert environments.
Despite their many benefits, tepary beans are not widely available in mainstream grocery stores. However, they can be found at some specialty food stores, farmers’ markets, and online retailers.
8. Acorn
When most people think of acorns, they probably picture them as a snack for squirrels and other wildlife. However, acorns are also a valuable food source for humans, particularly in desert regions where other food options may be scarce.
Acorns come from oak trees, which are found in many desert regions throughout the world. They are a nutrient-dense food, high in healthy fats, protein, and carbohydrates. They are also a good source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin E, magnesium, and potassium.
To prepare acorns for eating, they must first be leached to remove their bitter tannins. This can be done by soaking the acorns in water or boiling them multiple times. Once the tannins are removed, the acorns can be roasted or ground into flour to use in a variety of recipes, such as bread, pancakes, and porridge.
Aside from their nutritional value, acorns also have cultural and historical significance. Many indigenous communities throughout the world have relied on acorns as a staple food source for centuries. In addition, oak trees and acorns have played an important role in mythology and folklore, representing strength, longevity, and fertility.
However, it’s important to note that not all types of acorns are safe for consumption. Some species of oak trees produce acorns that are toxic to humans and animals, so it’s important to properly identify and select safe acorns for consumption.
Related: How To Find Water In The Desert With A Stick
9. Edible Cactus
When most people think of cacti, they imagine thorny plants that are impossible to touch, let alone eat. However, many types of cactus are actually edible and have been used as a food source for centuries by indigenous people. In fact, the prickly pear cactus, also known as nopal, is a staple food in many Latin American countries.
So, what parts of the cactus are edible? The most common edible parts of cacti are the pads, fruit, and flowers. The pads, also known as nopales, can be eaten raw or cooked and have a slightly tart, green bean-like flavor. They are rich in vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants, making them a nutritious addition to any meal.
Nopales can be sliced and used in salads, stir-fries, or grilled as a side dish. They can also be boiled or roasted to make a delicious, tangy soup.
The fruit of the cactus, known as the prickly pear, is a sweet and juicy treat that is packed with vitamins and minerals. The fruit can be eaten raw, cooked, or turned into jams, jellies, or syrup. The fruit’s seeds, which are high in protein and healthy fats, can also be roasted and eaten.
Finally, the flowers of some cacti, such as the saguaro, are edible and have a mild, sweet taste. They can be eaten raw or cooked and are often used in salads or as a garnish. The flowers can also be dried and ground into flour for baking.
It’s important to note that not all cacti are edible, and some can be toxic. It’s essential to know how to identify edible cacti and take the necessary precautions when harvesting them. In general, it’s best to stick to commonly eaten varieties and seek guidance from experienced foragers or experts.
